Cloud Computing : THE Definition
After several years of discussion and 15 different drafts and now globally accepted as the definition of Cloud Computing, NIST finally came up with the following definition of Cloud Computing:
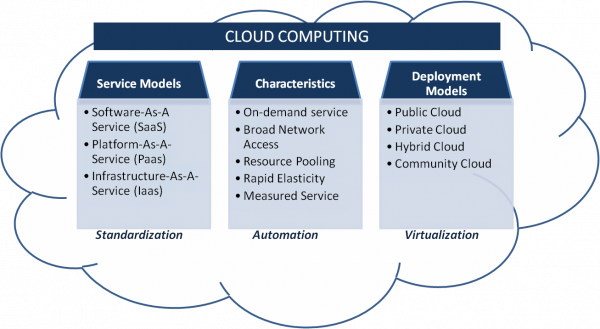
“Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model is composed of five essential characteristics, three service models, and four deployment models.”
A much simpler layman’s description of what Cloud Computing is might be: ……the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, security and more, via the the Internet.
Companies that offer these technology services are Cloud Service Providers (CSP), C-NEST is a CSP. We design, implement, deliver and charge for cloud computing resource on a utility basis, very similar to how you are e.g. billed for electricity at home or within your business.
Cloud Service Models
Cloud Service Models Cloud computing, whether supporting a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) or Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), or other variant, incorporates numerous hardware, software, middleware, security, monitoring and other capabilities to ensure application and information processing performance and reliability.
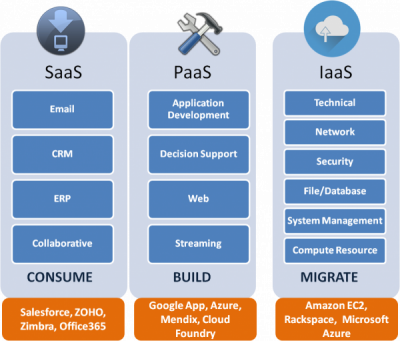
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) SaaS refers to the actual delivery model of applications across the Internet to end-users. A SaaS provider’s backend platform is usually associated with a simplified, dedicated environment. Today, SaaS is a common delivery model for most business applications, including accounting, collaboration, customer relationship management, enterprise resource planning and many more.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) PaaS provides the underlying hardware and software infrastructure configured and ready to go for application deployment. A PaaS service typically includes a development tool so application developers can build, test and design applications at a low coat instead of managing the infrastructure.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) IaaS supplies the entire underlying hardware and software infrastructure, excluding the operating system. IaaS typically relates to usage of physical server and storage capacity provided through virtual machines. Customers of IaaS are essentially renting space to load their preferred operating environment and applications. This is a cost-effective delivery model, where the service provider is responsible for owning, hosting, running and maintaining the equipment. Organizations typically pay only for what they use. IaaS is available as private, public or hybrid cloud hosting.
Other models Additional cloud computing models may include more specialized elements, such as a Compliance Cloud, which supports certain compliance requirements for specific industries or market segments (e.g., HIPAA compliance for healthcare), or mandated geographical boundaries such as municipal, state or federal legal compliance requirements, and foreign government regulations.
Types Of Cloud Deployment
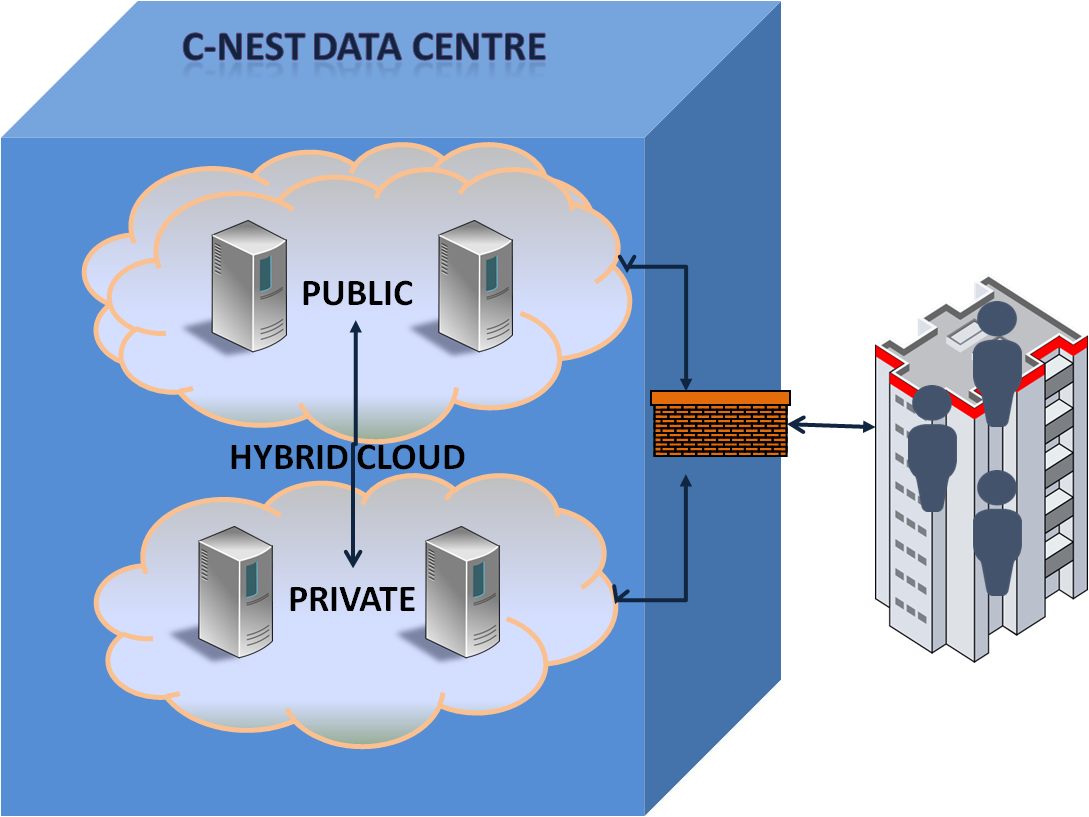
Hybrid Clouds are typically considered a combination of Private Clouds and Public Clouds.
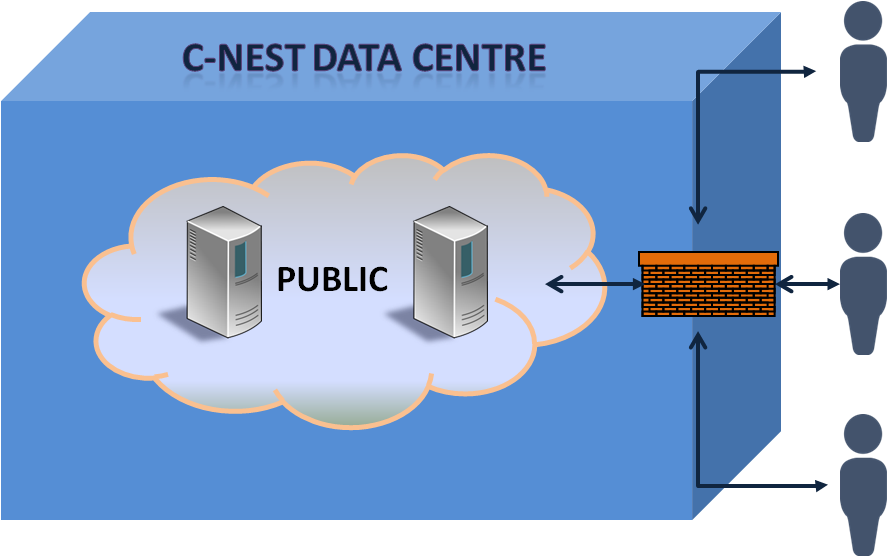
Public Cloud These are owned and operated by a third-party Cloud Service Provider (such as C-NEST). CPS’s deliver computing resources such as servers and storage over the Internet. In a Public Cloud deployment the hardware, software and other necessary infrastructure is owned and operated by the CSP. The cloud consumer (you!), can access these services and manage their cloud resources accounts via web browsers.
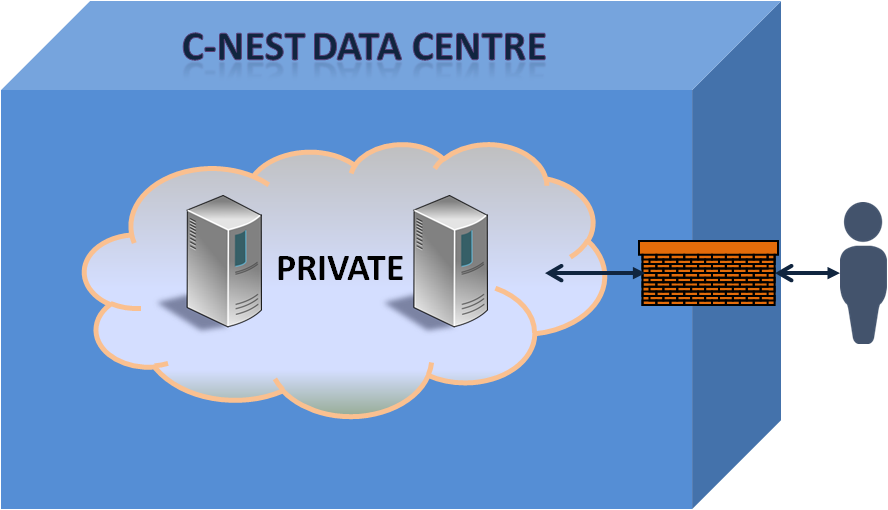
Private Cloud A private cloud refers to cloud computing resources used exclusively by a single business or organisation. A private cloud can be physically located on the company’s on-site data-center. Some companies also pay third-party service providers to host their private cloud. A private cloud is one in which the services and infrastructure are maintained on a private network
Hybrid Cloud Hybrid clouds combine public and private clouds, bound together by technology that allows data and applications to be shared between them. By allowing data and applications to move between private and public clouds, hybrid cloud gives businesses greater flexibility and more deployment options.